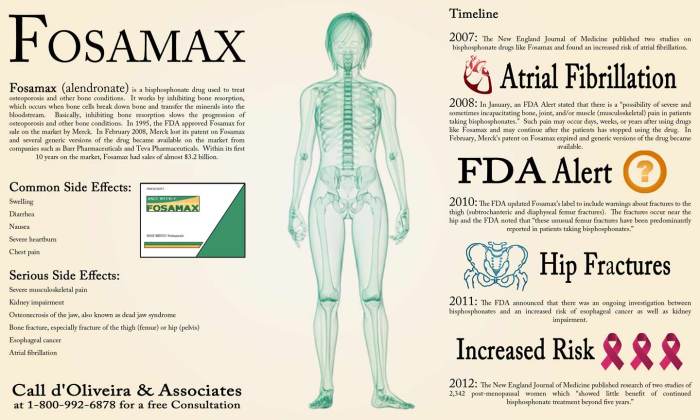
Fosamax side effects are a crucial aspect of understanding this medication, which is prescribed for osteoporosis. While Fosamax effectively helps strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects. This article explores the common and rare side effects, factors that may influence their occurrence, and strategies for managing them.
Fosamax works by slowing down the breakdown of bone tissue, allowing for stronger bones to form. It’s available in both oral tablet and intravenous infusion forms. However, like any medication, Fosamax can have side effects, ranging from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to more serious conditions like jawbone necrosis. Understanding these side effects is vital for making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
While Fosamax is generally safe and effective for treating osteoporosis, there are some rare but serious side effects that you should be aware of. One such side effect is jawbone necrosis, also known as osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Jawbone Necrosis (Osteonecrosis of the Jaw)
Jawbone necrosis is a condition where the bone in the jaw dies due to a lack of blood supply. This can happen when the blood vessels in the jaw are damaged, which can be caused by several factors, including certain medications, such as bisphosphonates like Fosamax.
- Risk Factors:
- Dental Procedures: People who have had recent dental procedures, such as tooth extractions, are at an increased risk of developing jawbone necrosis. This is because the procedure can damage the blood vessels in the jaw.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene, such as not brushing and flossing regularly, can also increase the risk of jawbone necrosis. This is because bacteria in the mouth can infect the jawbone, which can damage the blood vessels.
- Cancer: People who have cancer and are undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy are also at an increased risk of developing jawbone necrosis. This is because these treatments can damage the blood vessels in the jaw.
- Steroid Use: Long-term use of steroids can also increase the risk of jawbone necrosis.
- Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for many health problems, including jawbone necrosis. Smoking can damage the blood vessels and make it more difficult for the jawbone to heal.
- Symptoms:
- Pain: The most common symptom of jawbone necrosis is pain in the jaw. This pain may be persistent or intermittent, and it may worsen when chewing.
- Swelling: The jaw may also become swollen.
- Loose Teeth: If the jawbone is damaged, the teeth may become loose.
- Open Sores: In some cases, open sores may develop on the gums or jawbone.
- Treatment:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be used to treat any infections in the jawbone.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged bone and to promote healing.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: This therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. It can help to increase blood flow to the jawbone and promote healing.
Side Effects and Patient Characteristics
It’s important to understand how factors like age, gender, and medical history can influence the likelihood and severity of Fosamax side effects. Additionally, knowing about potential drug interactions and precautions for individuals with specific health conditions can help ensure safe and effective treatment.
Age and Gender
Older adults may be more susceptible to certain side effects of Fosamax, such as atypical femur fractures. This is because bone density naturally decreases with age, making bones more fragile. While both men and women can experience side effects, some research suggests that women may be more likely to experience certain side effects, such as esophageal irritation.
Medical History
Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as gastrointestinal problems or kidney disease, may be at increased risk for certain side effects. For instance, those with a history of esophageal disorders may be more prone to esophageal irritation or ulcers. It’s crucial to discuss your medical history with your doctor to determine if Fosamax is appropriate for you.
Drug Interactions
Fosamax can interact with other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. For example, taking Fosamax with certain antibiotics or medications that affect calcium levels in the blood can increase the risk of side effects. It’s essential to inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, you are taking.
Precautions for Specific Health Conditions
Individuals with certain health conditions require special considerations when taking Fosamax. For example, people with esophageal disorders should take Fosamax with a full glass of water and remain upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication to minimize the risk of esophageal irritation. Similarly, individuals with kidney problems may require dosage adjustments to prevent potential complications.
Managing Side Effects
It’s important to understand that while Fosamax can be effective in treating osteoporosis, it can also cause side effects. Many of these side effects are mild and can be managed with simple lifestyle changes. However, some side effects can be more serious and require medical attention.
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Gastrointestinal discomfort, such as heartburn, indigestion, and stomach pain, is a common side effect of Fosamax. These side effects are often caused by the way Fosamax is absorbed into the body.
- Take Fosamax with a full glass of water: This helps to ensure that the medication is properly absorbed and reduces the risk of irritation in the esophagus.
- Take Fosamax on an empty stomach: This is usually recommended to maximize absorption. However, it’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions.
- Avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking Fosamax: This helps to prevent the medication from refluxing back into the esophagus.
- Consider taking Fosamax at bedtime: This can reduce the risk of gastrointestinal discomfort, as you are less likely to eat or drink anything after taking the medication.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in minimizing side effects associated with Fosamax.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone health and can help to reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
- Engage in regular exercise: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and dancing, help to strengthen bones and improve overall health.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: These habits can negatively impact bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Treatment Options
If you experience persistent or severe side effects, it’s crucial to consult your doctor. They may recommend treatment options to manage these side effects, such as:
- Antacids: These medications can help to neutralize stomach acid and reduce heartburn.
- H2 blockers: These medications reduce the production of stomach acid.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These medications block the production of stomach acid for a longer duration than H2 blockers.
Long-Term Side Effects: Fosamax Side Effects
While Fosamax is generally safe and effective for treating osteoporosis, it’s important to be aware of the potential long-term side effects that can occur with prolonged use. Some side effects might not be noticeable immediately but can develop over time.
Regular monitoring is crucial to detect any potential side effects early on. This includes regular checkups with your healthcare provider, where you can discuss any changes in your health or any concerns you may have.
Understanding Long-Term Side Effects
Long-term use of Fosamax can increase the risk of certain side effects, including:
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ): This is a rare but serious condition where bone in the jaw dies due to poor blood supply. It’s more likely to occur in people who have had dental procedures, such as tooth extractions or implants, while taking Fosamax.
- Atypical Femoral Fractures: These are fractures that occur in the thigh bone, often in the upper part, and are more common in people taking bisphosphonates like Fosamax.
- Esophageal Problems: Fosamax can irritate the esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach. This can lead to inflammation, ulcers, or even narrowing of the esophagus.
- Low Blood Calcium: In rare cases, Fosamax can cause a decrease in blood calcium levels, which can lead to symptoms such as muscle cramps, fatigue, and confusion.
- Eye Problems: Some people taking Fosamax have reported eye problems, such as inflammation of the eye or blurred vision.
Fosamax and Pregnancy/Breastfeeding
Fosamax (alendronate) is a medication used to treat osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures. While Fosamax is effective in treating osteoporosis, its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is a matter of concern due to potential risks to the developing fetus and infant.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of Fosamax with your doctor before taking it if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Fosamax and Pregnancy
Fosamax is categorized as a pregnancy category C medication, meaning that animal studies have shown adverse effects on the fetus, but there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in humans.
While the risks of Fosamax use during pregnancy are not fully understood, there are potential concerns:
- Bone Development: Fosamax can interfere with bone development in the fetus, potentially leading to skeletal abnormalities.
- Other Potential Risks: There is a possibility of other adverse effects on the developing fetus, although these have not been definitively established.
Because of these potential risks, Fosamax is generally not recommended for use during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Fosamax and Breastfeeding
Fosamax is excreted in breast milk in small amounts. However, the potential risks to a breastfeeding infant are unknown.
- Limited Data: There is limited information available about the effects of Fosamax on breastfeeding infants.
- Potential Risks: While the amount of Fosamax in breast milk is low, there is a possibility of adverse effects on the infant’s bone development or other health issues.
It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of Fosamax with your doctor before taking it if you are breastfeeding.
Alternative Treatments During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding and need treatment for osteoporosis, your doctor may recommend alternative therapies that are considered safer for you and your baby. These may include:
- Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: These are essential nutrients for bone health and are generally safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Lifestyle Modifications: This may include regular weight-bearing exercise, smoking cessation, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
- Other Medications: Your doctor may consider other osteoporosis medications that are considered safer during pregnancy and breastfeeding, such as bisphosphonates like risedronate (Actonel) or ibandronate (Boniva).
Fosamax and Other Medications

Fosamax can interact with other medications, potentially affecting how they work or increasing the risk of side effects. It’s crucial to inform your healthcare professional about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements. This information helps your doctor determine the best course of treatment for you and manage any potential interactions.
Potential Interactions
Understanding the potential interactions between Fosamax and other medications is essential for safe and effective treatment. Certain medications can interfere with the absorption of Fosamax, while others may increase the risk of side effects.
- Antacids: Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium can interfere with the absorption of Fosamax. It’s recommended to take Fosamax at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after taking antacids.
- Calcium Supplements: While calcium is necessary for bone health, taking calcium supplements at the same time as Fosamax can reduce its absorption. It’s advisable to take Fosamax at least 30 minutes before or 2 hours after taking calcium supplements.
- Other Medications: Certain medications, such as bisphosphonates (e.g., Actonel, Boniva), estrogen replacement therapy, and some antibiotics, can interact with Fosamax. Discuss any other medications you’re taking with your healthcare provider.
Patient Education and Awareness
Fosamax (alendronate) is a medication used to treat and prevent osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures. It is important to understand how Fosamax works, its potential side effects, and how to use it safely.
Understanding Fosamax
Fosamax is a type of medication called a bisphosphonate. It works by slowing down the breakdown of bone, which helps to increase bone density and strength. This can reduce the risk of fractures.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects of Fosamax can include:
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Stomach pain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Muscle or joint pain
These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own.
Serious Side Effects
Serious side effects of Fosamax are rare but can be serious. These include:
- Esophageal irritation or ulcers
- Jawbone problems (osteonecrosis of the jaw)
- Atypical fractures of the femur
- Low levels of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia)
If you experience any of these serious side effects, stop taking Fosamax and contact your doctor immediately.
Table of Common and Serious Side Effects, Fosamax side effects
| Side Effect | Common | Serious |
|---|---|---|
| Heartburn | X | |
| Indigestion | X | |
| Stomach pain | X | |
| Nausea | X | |
| Diarrhea | X | |
| Constipation | X | |
| Muscle or joint pain | X | |
| Esophageal irritation or ulcers | X | |
| Jawbone problems (osteonecrosis of the jaw) | X | |
| Atypical fractures of the femur | X | |
| Low levels of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia) | X |
Resources for More Information
If you have questions about Fosamax or its side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. You can also find more information on the following websites:
- National Osteoporosis Foundation: https://www.nof.org/
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration: https://www.fda.gov/
Fosamax and Osteoporosis Management
Fosamax (alendronate) is a medication used to treat and prevent osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures. It works by slowing down the rate at which bone is broken down, which helps to increase bone density and strength.
Importance of Following Prescribed Treatment Regimens
Following your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and frequency of Fosamax is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing the risk of side effects. Skipping doses or taking more than prescribed can hinder the medication’s ability to build bone density and increase the risk of fractures.
Lifestyle Modifications to Complement Fosamax Therapy
Lifestyle changes can significantly complement Fosamax therapy in managing osteoporosis.
- Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise: Activities such as walking, jogging, dancing, and weightlifting help to strengthen bones.
- Calcium-Rich Diet: Consuming calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods ensures adequate calcium intake for bone health.
- Vitamin D Supplementation: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, making supplementation necessary, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking negatively impacts bone health, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Quitting smoking can significantly improve bone density and reduce fracture risk.
- Alcohol Moderation: Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures. Limiting alcohol intake is essential for maintaining bone health.
Navigating the potential side effects of Fosamax requires open communication with your healthcare provider. They can help you weigh the benefits of Fosamax against the risks and create a personalized treatment plan. Remember, proactive management and informed decision-making are key to maximizing the benefits of Fosamax while minimizing the potential for side effects. By understanding the potential risks and taking appropriate precautions, you can confidently manage your osteoporosis with Fosamax.
Fosamax, a medication used to treat osteoporosis, can have side effects like jawbone problems and digestive issues. While it’s important to discuss any concerns with your doctor, you may also want to consider alternative treatments like over-the-counter pain relievers, such as celebrex 200 mg , which can help manage pain and inflammation associated with osteoporosis. It’s crucial to remember that Fosamax can interact with other medications, so always consult your doctor before starting any new treatment.