SSRI side effects are a common concern for individuals taking these medications for mental health conditions. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of antidepressants that work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. While SSRIs can be highly effective for many people, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential side effects that may accompany their use.
This comprehensive guide will explore the various side effects associated with SSRIs, including common and less frequent ones, as well as potential long-term implications. We will delve into the mechanisms behind these side effects, discuss strategies for managing them, and provide valuable information for patients taking SSRIs.
Understanding SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of antidepressants that are commonly prescribed for a range of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
SSRIs work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other important functions. By increasing serotonin levels, SSRIs help to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Mechanism of Action of SSRIs
SSRIs work by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is released from nerve cells (neurons) and travels across a gap called a synapse to bind to receptors on other neurons. After serotonin has done its job, it is normally reabsorbed back into the presynaptic neuron, a process called reuptake. SSRIs block this reuptake process, allowing serotonin to remain in the synapse for a longer period of time. This increased serotonin activity is thought to be responsible for the therapeutic effects of SSRIs.
Common SSRI Medications
SSRIs are a widely used class of antidepressants, and there are several different medications available. Some common SSRI medications include:
- Fluoxetine (Prozac): Fluoxetine is one of the most commonly prescribed SSRIs. It is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, bulimia nervosa, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD).
- Sertraline (Zoloft): Sertraline is another widely prescribed SSRI. It is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, OCD, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Paroxetine (Paxil): Paroxetine is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, OCD, and panic disorder.
- Citalopram (Celexa): Citalopram is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and panic disorder.
- Escitalopram (Lexapro): Escitalopram is a newer SSRI that is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
Differences Between SSRIs and Other Antidepressants
SSRIs are just one type of antidepressant. Other types of antidepressants include:
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): TCAs are older antidepressants that work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. TCAs are less commonly prescribed than SSRIs due to their side effects, which can include drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOIs are a class of antidepressants that work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase. MAOIs are rarely prescribed due to their potential for dangerous interactions with certain foods and medications.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): SNRIs are a newer class of antidepressants that work by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. SNRIs are often effective in treating depression, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain.
Common Side Effects
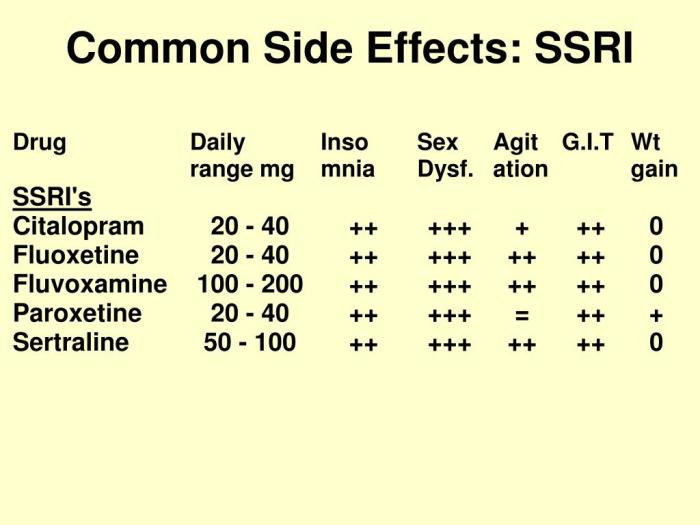
It’s important to understand that everyone reacts differently to medications, and not everyone taking SSRIs will experience side effects. However, some side effects are more common than others.
These side effects can vary in severity and duration, with some being mild and short-lived, while others can be more intense and persistent. It’s crucial to discuss any concerns you have with your doctor, as they can help manage these side effects and adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Gastrointestinal issues are among the most frequently reported side effects of SSRIs. These can include:
- Nausea: Feeling queasy or sick to your stomach is a common side effect, particularly in the early stages of treatment. This usually subsides within a few weeks as your body adjusts to the medication.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation, can also occur. These are often temporary and may resolve on their own.
- Loss of Appetite: Some individuals may experience a decrease in appetite, leading to weight loss. This can be a concern, especially if it’s significant or persistent.
- Dry Mouth: A dry mouth is another common side effect, which can be uncomfortable but usually resolves on its own.
Neurological Side Effects
SSRIs can also affect the nervous system, leading to side effects such as:
- Headache: Headaches are a common side effect, often mild and temporary. They may be more frequent or severe in the early stages of treatment.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy is another common side effect, particularly when standing up quickly. This usually subsides within a few weeks as your body adjusts to the medication.
- Insomnia or Sleep Disturbances: Some individuals may experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, or they may wake up earlier than usual. This can be due to the stimulating effects of some SSRIs.
- Tremors: Slight tremors or shaking may occur, especially in the hands. These are usually mild and tend to subside with time.
- Sexual Side Effects: These can include decreased libido, difficulty achieving an erection, or delayed ejaculation. These side effects can be distressing, but there are often ways to manage them.
Emotional and Psychological Side Effects
While SSRIs are generally effective in treating depression and anxiety, some individuals may experience emotional and psychological side effects, such as:
- Anxiety: Paradoxically, some individuals may experience increased anxiety in the early stages of treatment. This is usually temporary and tends to subside as the medication takes effect.
- Agitation: Feeling restless or agitated is another possible side effect. This may be more common in the early stages of treatment.
- Mood Swings: Fluctuations in mood can occur, ranging from heightened emotions to feelings of irritability.
Side Effects by Medication: Ssri Side Effects
It’s important to remember that everyone reacts differently to medications, and the severity of side effects can vary widely. This table provides a general overview of common side effects associated with different SSRIs. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to discuss any concerns you may have.
Common Side Effects by SSRI Medication
| Medication Name | Side Effect | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Fluoxetine (Prozac) | Nausea, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, sexual dysfunction | Mild to moderate |
| Sertraline (Zoloft) | Diarrhea, dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, anxiety | Mild to moderate |
| Paroxetine (Paxil) | Weight gain, sweating, tremor, agitation, sexual dysfunction | Mild to moderate |
| Citalopram (Celexa) | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, anxiety | Mild to moderate |
| Escitalopram (Lexapro) | Drowsiness, fatigue, insomnia, sexual dysfunction, weight gain | Mild to moderate |
Withdrawal Symptoms
Discontinuing SSRI medication can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can be uncomfortable and sometimes even severe. These symptoms typically occur when the medication is stopped abruptly or tapered off too quickly. It’s crucial to understand the potential withdrawal symptoms and work with your doctor to develop a safe tapering plan.
Understanding Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms from SSRIs are often described as a “rebound effect” where the body experiences the opposite effects of the medication. This can be due to the brain adjusting to the presence of the medication and then experiencing a withdrawal effect when it’s no longer present. These symptoms can vary in severity and duration, depending on the individual, the type of SSRI, and the dosage.
Common Withdrawal Symptoms
Common withdrawal symptoms from SSRIs include:
- Flu-like symptoms (headache, fatigue, muscle aches)
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or vertigo
- Insomnia or vivid dreams
- Anxiety, irritability, or restlessness
- Sensory disturbances (tingling, numbness, or electric shock sensations)
- Mood swings or emotional lability
Tips for Safely Tapering Off SSRI Medication
- Discuss with your doctor: It’s essential to discuss your plan to discontinue SSRIs with your doctor. They can help you develop a safe and gradual tapering schedule based on your individual needs and medical history.
- Gradual reduction: Instead of stopping the medication abruptly, your doctor may recommend reducing your dosage gradually over several weeks or months. This allows your body to adjust to the decreasing levels of medication.
- Monitor for symptoms: Be aware of any potential withdrawal symptoms and report them to your doctor immediately. They may need to adjust your tapering schedule or address any concerning symptoms.
- Consider alternative treatments: If you experience severe withdrawal symptoms, your doctor may consider alternative treatments, such as non-pharmacological therapies or different medications.
Severity of Withdrawal Symptoms
The severity of withdrawal symptoms can vary between different SSRIs. Some SSRIs, such as paroxetine (Paxil), are known to have more pronounced withdrawal symptoms compared to others.
It’s important to note that withdrawal symptoms can vary widely between individuals, and not everyone will experience them.
Interactions with Other Medications
SSRIs can interact with various other medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This includes prescription medications, as well as any recreational drugs you may be using.
Interactions with Other Medications
Understanding potential interactions between SSRIs and other medications is vital for safe and effective treatment. Certain combinations can lead to increased side effects, decreased effectiveness of either medication, or even serious health risks.
Interactions with Other Medications
- MAOIs (Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors): Combining SSRIs with MAOIs, such as phenelzine (Nardil) or tranylcypromine (Parnate), can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by symptoms like confusion, agitation, fever, sweating, and muscle rigidity. It’s crucial to avoid using MAOIs within two weeks of stopping an SSRI, and vice versa.
- Triptans: Triptans, medications used to treat migraines, can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome when combined with SSRIs. This interaction is more likely if you’re taking high doses of either medication.
- Other Serotonergic Medications: Combining SSRIs with other medications that increase serotonin levels, such as tramadol (Ultram), lithium (Lithobid), and certain antidepressants, can also increase the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Blood Thinners: SSRIs can interact with blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin) and increase the risk of bleeding. Your doctor may need to adjust your blood thinner dosage if you’re taking an SSRI.
- Antipsychotics: Some antipsychotics, such as haloperidol (Haldol), can increase the risk of movement disorders when combined with SSRIs.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal remedies, like St. John’s wort, can interact with SSRIs and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. It’s important to discuss any herbal remedies you’re using with your doctor.
Guidelines for Safe Medication Use
- Be Open and Honest with Your Doctor: Tell your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This includes prescription medications, as well as any recreational drugs you may be using.
- Don’t Stop Taking Medications Without Consulting Your Doctor: Abruptly stopping an SSRI can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your medication regimen.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Pay attention to any changes in your health while taking SSRIs. Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions: Take your medications as prescribed and follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. This includes taking the correct dosage, at the right time, and for the prescribed duration.
Long-Term Side Effects
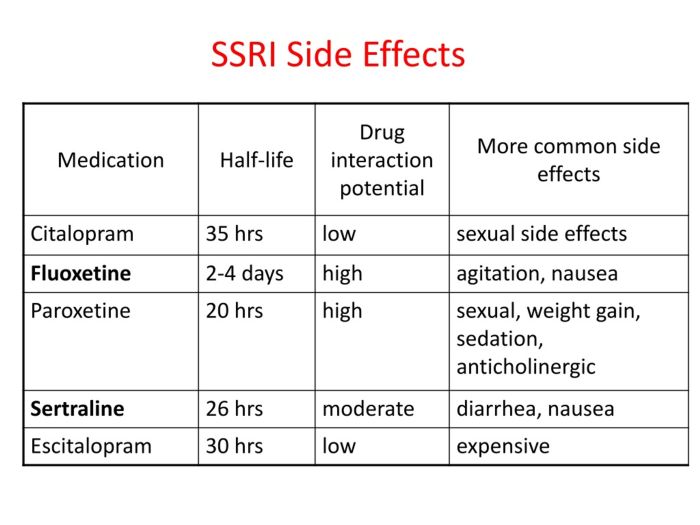
While SSRIs are generally safe for short-term use, their long-term effects are less well understood. It’s crucial to weigh the potential risks and benefits of long-term SSRI therapy, especially considering the possibility of developing long-term side effects.
Long-Term Side Effects of SSRIs, Ssri side effects
Long-term SSRI use, which is defined as taking these medications for more than a year, can potentially lead to a range of side effects. Some of these side effects may persist even after discontinuing the medication.
- Sexual dysfunction: This is a common side effect that can persist even after stopping SSRIs. It may manifest as decreased libido, difficulty achieving orgasm, or erectile dysfunction.
- Weight gain: SSRIs can affect appetite and metabolism, leading to weight gain in some individuals. This can be a particular concern for people with a history of eating disorders or weight management issues.
- Metabolic syndrome: Long-term SSRI use has been linked to an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Abruptly stopping SSRIs after long-term use can trigger withdrawal symptoms like dizziness, nausea, anxiety, and insomnia. This is why it’s essential to taper off SSRIs gradually under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Dependence: While SSRIs are not considered addictive in the traditional sense, long-term use can lead to dependence. This means that the body may become accustomed to the medication, and stopping it abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
- Increased risk of falls: Some studies suggest that long-term SSRI use may increase the risk of falls, especially in older adults. This is likely due to the medication’s effects on balance and coordination.
Research Findings on Long-Term SSRI Use
Research on the long-term effects of SSRIs is ongoing. While some studies have shown potential risks associated with long-term use, others have found no significant adverse effects. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term impact of these medications.
Comparing Risks and Benefits of Long-Term SSRI Therapy
The decision to continue long-term SSRI therapy is a complex one that involves weighing the potential risks against the benefits. It’s crucial to have an open and honest conversation with your healthcare provider to discuss your individual situation and make an informed decision.
- Benefits: For individuals with chronic mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, or obsessive-compulsive disorder, long-term SSRI therapy can provide significant relief and improve quality of life. The benefits of continued treatment may outweigh the potential risks, especially if the individual experiences significant improvement in their symptoms.
- Risks: As discussed earlier, long-term SSRI use can carry potential risks, including the development of long-term side effects. It’s important to be aware of these risks and to monitor for any changes in your health while taking SSRIs.
Risk Factors for Side Effects
Not everyone who takes an SSRI will experience side effects, and the severity of side effects can vary greatly from person to person. Several factors can influence the likelihood of experiencing side effects, including individual characteristics, the specific SSRI medication being taken, and other medications or substances being used.
Factors that Increase the Risk of Side Effects
It is important to understand the factors that can increase the risk of experiencing side effects, as this information can help healthcare providers make more informed decisions about treatment.
- Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to some side effects, particularly those related to the central nervous system, such as confusion, dizziness, and falls.
- Gender: Women may be more likely to experience certain side effects, such as sexual dysfunction, than men.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have genetic predispositions that make them more likely to experience certain side effects. For example, certain genetic variations may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur with SSRI use.
- Medical History: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, liver disease, or kidney disease, may be at increased risk for certain side effects.
- Other Medications: Taking other medications, including over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and illicit drugs, can interact with SSRIs and increase the risk of side effects.
- Dosage: Higher doses of SSRIs are generally associated with a higher risk of side effects.
- Route of Administration: Some SSRIs are available in different forms, such as tablets, capsules, and liquid formulations. The route of administration can influence the rate of absorption and the risk of certain side effects.
Managing Side Effects
It’s common to experience side effects when starting an SSRI, but many can be managed. Remember, everyone responds differently to medication, so what works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to communicate with your doctor about any side effects you’re experiencing so they can help you find the best course of action.
Strategies for Managing Side Effects
There are various strategies you can use to manage or mitigate SSRI side effects. These strategies are often used in combination to achieve the best results.
- Adjusting Dosage: Your doctor may adjust your dosage, either increasing or decreasing it, to find the right balance between symptom relief and side effects.
- Switching Medications: If the side effects are severe or persist, your doctor may suggest switching to a different SSRI or a different type of antidepressant altogether.
- Time: Some side effects may subside over time as your body adjusts to the medication. It’s essential to be patient and work with your doctor to determine the best course of action.
- Non-Pharmacological Strategies: In addition to medication, there are other things you can do to manage side effects. These strategies can be particularly helpful for mild side effects or in combination with medication.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing SSRI side effects. These changes can help alleviate symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
- Diet and Exercise: A healthy diet and regular exercise can help improve mood, energy levels, and sleep quality, which can contribute to managing side effects.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed can improve sleep quality, which can help manage side effects like insomnia.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can be helpful for managing side effects like nervousness and agitation.
Available Resources and Support Groups
If you’re struggling with SSRI side effects, it’s important to know that you’re not alone. There are resources and support groups available to help you cope and manage these challenges.
- Talk to your Doctor: Your doctor is your primary resource for managing side effects. They can provide guidance, adjust your medication, and refer you to other specialists if needed.
- Therapist or Counselor: A therapist can provide emotional support and help you develop coping strategies for managing side effects.
- Support Groups: Online and in-person support groups can connect you with others who understand what you’re going through and provide a sense of community.
- Mental Health Organizations: Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the American Psychiatric Association (APA) offer resources and information about mental health conditions and medication management.
Patient Information
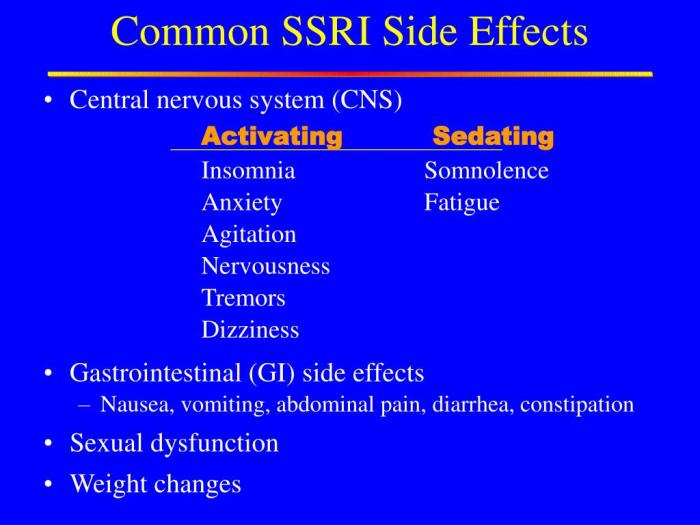
This guide provides essential information for patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Understanding the potential side effects, management strategies, and interactions is crucial for maximizing the benefits of SSRI therapy while minimizing risks.
Side Effects
Side effects are common with SSRIs, and their severity can vary depending on the individual and the specific medication.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and stomach upset are frequent side effects.
- Sexual Side Effects: Decreased libido, difficulty achieving orgasm, and erectile dysfunction can occur in some patients.
- Emotional Changes: Anxiety, agitation, insomnia, and restlessness are possible side effects.
- Physical Symptoms: Headache, dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and tremors are common.
- Weight Changes: Some SSRIs can lead to weight gain or loss.
Managing Side Effects
Most side effects are mild and tend to subside within a few weeks as your body adjusts to the medication. However, if side effects persist or become bothersome, it’s important to discuss them with your doctor.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can help alleviate some side effects.
- Medication Adjustments: Your doctor may adjust the dosage or switch you to a different SSRI if side effects are severe.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Over-the-counter medications like antacids, antihistamines, and sleep aids can help manage certain side effects.
Interactions with Other Medications
SSRIs can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and illicit substances. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking, including prescription and non-prescription drugs, to avoid potentially dangerous interactions.
Patient Rights and Resources
Patients have the right to understand their medications and treatment options.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor or pharmacist any questions you have about your medication.
- Seek Additional Information: The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provide comprehensive information about SSRIs and mental health conditions.
- Patient Support Groups: Connecting with others who are taking SSRIs can provide support and valuable insights.
Navigating the world of SSRI side effects requires a balance of understanding and proactive management. By being informed about the potential risks and benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment, discuss concerns with their healthcare providers, and work together to find the best approach for their individual needs. Remember, open communication and a collaborative approach are key to maximizing the benefits of SSRI therapy while minimizing potential side effects.
SSRIs, while effective for many, can have a range of side effects, including nausea, weight changes, and sexual dysfunction. Some people find relief from these side effects by exploring alternative treatments like MS Contin , a long-acting opioid used for chronic pain management. However, it’s crucial to consult with a doctor to determine if MS Contin is an appropriate option and to discuss the potential risks and benefits of switching treatments.