Propranolol uses span a wide range of medical conditions, making it a versatile medication with significant impact on patient well-being. This beta-blocker, known for its ability to slow the heart rate and lower blood pressure, has found applications in treating everything from high blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms to anxiety disorders and migraines. Understanding propranolol’s uses and its potential benefits is crucial for patients seeking effective treatment options.
Propranolol’s mechanism of action involves blocking the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline, hormones that play a vital role in regulating heart rate, blood pressure, and other bodily functions. By interfering with these hormones, propranolol can effectively manage a variety of conditions, including those related to the cardiovascular system, nervous system, and endocrine system.
What is Propranolol?: Propranolol Uses
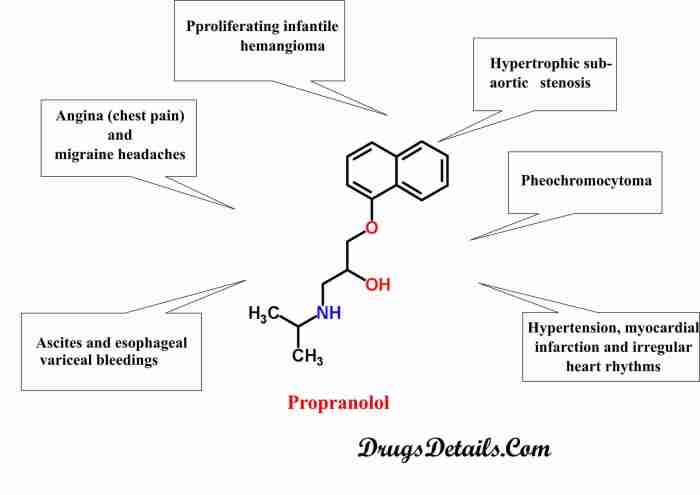
Propranolol is a medication commonly prescribed for a range of conditions, primarily those related to the cardiovascular system. It is a beta-blocker, meaning it blocks the effects of adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) on the heart and blood vessels. This action helps regulate heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital functions.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Propranolol is a synthetic compound with the chemical formula C16H21NO3. Its structure features a central aromatic ring connected to a secondary amine and a propanolamine side chain. This structure is responsible for its pharmacological properties. Propranolol is a white, crystalline powder that is practically insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and other organic solvents.
Mechanism of Action
Propranolol exerts its effects by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, specifically beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. These receptors are located throughout the body, particularly in the heart, blood vessels, lungs, and liver. When adrenaline or noradrenaline binds to these receptors, they trigger a cascade of events that lead to various physiological responses.
Propranolol acts as an antagonist, blocking the binding of adrenaline and noradrenaline to these receptors. This prevents the activation of the signaling pathways that would normally occur.
Classification as a Beta-Blocker
Propranolol is classified as a non-selective beta-blocker, meaning it blocks both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. This contrasts with selective beta-blockers, which primarily target beta-1 receptors.
Role in the Cardiovascular System, Propranolol uses
Propranolol plays a crucial role in regulating cardiovascular function. Its action on beta-1 receptors in the heart leads to:
* Reduced heart rate: By blocking the stimulatory effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline on the heart, propranolol slows down the heart rate.
* Decreased contractility: Propranolol also reduces the force of contraction of the heart muscle, leading to a decrease in cardiac output.
* Lowered blood pressure: By reducing heart rate and contractility, propranolol indirectly contributes to lowering blood pressure.
Propranolol stands as a testament to the power of medication in improving human health. Its diverse applications, ranging from managing heart conditions to easing anxiety and preventing tremors, highlight its importance in modern medicine. While propranolol offers significant benefits, it’s crucial to remember that it’s not a cure-all. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine if propranolol is the right treatment option for your specific needs.
Propranolol is a beta-blocker often prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure and anxiety. While it’s generally well-tolerated, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. In contrast, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like paroxetine can also cause side effects, which you can learn more about here. Understanding these potential side effects can help you make informed decisions about your medication and discuss any concerns with your doctor.