SGLT2 inhibitors have revolutionized diabetes management by offering a novel approach to lowering blood sugar levels. These medications work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in urine. This mechanism of action makes SGLT2 inhibitors particularly effective in patients with type 2 diabetes, especially those with additional cardiovascular risk factors.
Beyond their primary role in blood sugar control, SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated significant benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk, improving heart function in patients with heart failure, and even protecting kidney health. Their versatility and effectiveness have made them a cornerstone of modern diabetes care, prompting ongoing research to further explore their potential applications and optimize their use in diverse patient populations.
Illustrative Case Studies
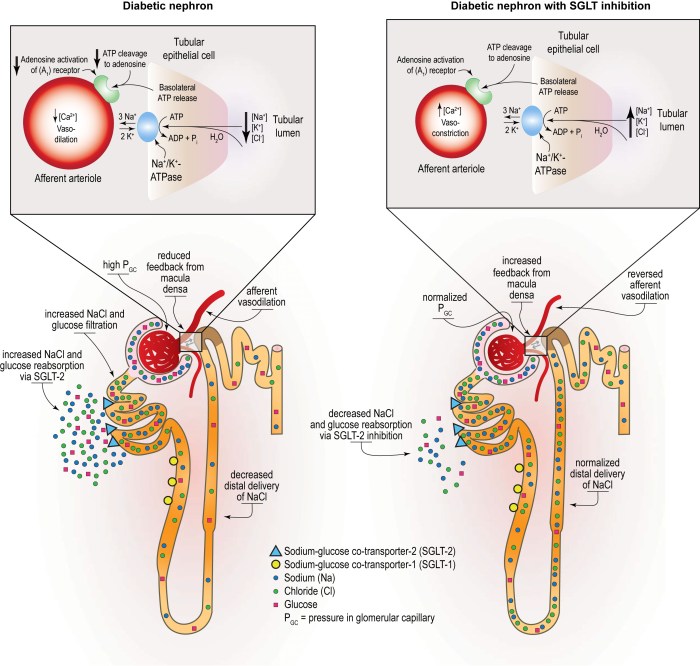
SGLT2 inhibitors have demonstrated their efficacy in managing type 2 diabetes, but their benefits extend beyond glycemic control. This section explores real-world scenarios where SGLT2 inhibitors have made a significant impact on patient health.
Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Factors
This case study showcases the application of SGLT2 inhibitors in a patient with type 2 diabetes and co-existing cardiovascular risk factors.
Mr. Jones, a 62-year-old male with a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, presented with uncontrolled blood sugar levels despite lifestyle modifications and metformin therapy. He also had a family history of premature coronary artery disease, raising his cardiovascular risk.
After a thorough evaluation, Mr. Jones was started on an SGLT2 inhibitor alongside his existing medications.
- The SGLT2 inhibitor effectively lowered his blood sugar levels, improving his glycemic control.
- The medication also reduced his blood pressure and improved his lipid profile, mitigating his cardiovascular risk factors.
- Mr. Jones experienced a significant improvement in his overall health and well-being, with fewer complications associated with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
This case demonstrates the multifaceted benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
Heart Failure
This case study highlights the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in a patient with heart failure.
Ms. Smith, a 70-year-old female with a history of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, presented with symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention. Despite optimal medical management, she continued to experience recurrent hospitalizations.
Following a comprehensive assessment, Ms. Smith was started on an SGLT2 inhibitor.
- The SGLT2 inhibitor significantly reduced her hospitalizations and improved her quality of life.
- The medication also slowed the progression of her heart failure and improved her overall cardiovascular health.
This case underscores the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in improving outcomes for patients with heart failure.
Chronic Kidney Disease
This case study illustrates the potential benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in a patient with chronic kidney disease.
Mr. Lee, a 55-year-old male with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, was experiencing a decline in kidney function despite optimal medical management. He was at risk for further kidney damage and potential dialysis.
Mr. Lee was started on an SGLT2 inhibitor.
- The SGLT2 inhibitor slowed the progression of his kidney disease and preserved his kidney function.
- The medication also improved his blood sugar control and reduced his cardiovascular risk.
This case demonstrates the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in protecting kidney function and improving outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Patient Education and Counseling
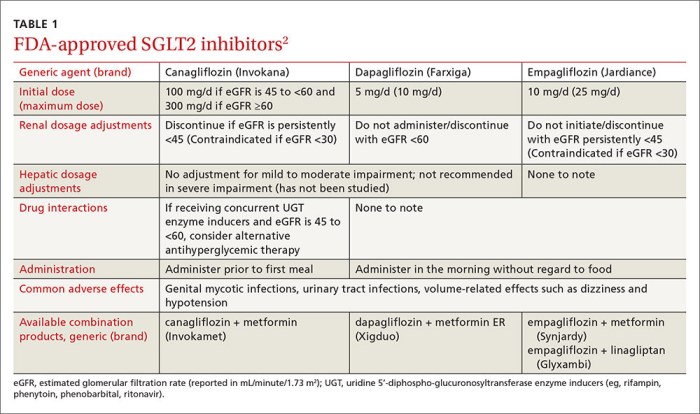
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications used to help manage type 2 diabetes. They work by helping your kidneys remove excess sugar from your blood, which lowers your blood sugar levels. They can also help you lose weight and lower your blood pressure.
Understanding SGLT2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors are a relatively new class of medications for type 2 diabetes. They are generally safe and effective, but it’s important to understand how they work, their potential side effects, and how to take them properly.
Key Information About SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Medication Names: Some common SGLT2 inhibitors include:
- Canagliflozin (Invokana)
- Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
- Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
- Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)
- Dosages: The dosage of SGLT2 inhibitors varies depending on the specific medication and your individual needs. Your doctor will determine the right dosage for you.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors include:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Yeast infections
- Dehydration
- Increased urination
In rare cases, SGLT2 inhibitors can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Ketoacidosis (a dangerous condition that occurs when your body produces too many ketones)
- Amputations (in people with diabetic foot ulcers)
It’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience any side effects, especially if they are severe or persistent.
- Potential Drug Interactions: SGLT2 inhibitors can interact with other medications, including:
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Certain blood thinners
- Insulin
It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements, before starting SGLT2 inhibitors.
SGLT2 Inhibitors: Benefits, Risks, and Management
This brochure provides information about SGLT2 inhibitors, a type of medication used to manage type 2 diabetes. It’s essential to understand the benefits, potential risks, and how to manage your treatment effectively.
Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors offer several benefits for people with type 2 diabetes, including:
- Lowering Blood Sugar: SGLT2 inhibitors help lower blood sugar levels by increasing the amount of sugar excreted in urine. This can help improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
- Weight Loss: SGLT2 inhibitors can help you lose weight by reducing your appetite and increasing the amount of calories you burn.
- Lowering Blood Pressure: Some SGLT2 inhibitors can also help lower blood pressure, which is a benefit for people with diabetes who are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Studies have shown that SGLT2 inhibitors can reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death in people with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Potential Risks of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Like all medications, SGLT2 inhibitors can cause side effects. The most common side effects are:
- Increased Urination: You may notice an increase in the frequency and amount of urine you produce. This is because SGLT2 inhibitors help your kidneys remove excess sugar from your blood through urine.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): SGLT2 inhibitors can increase the risk of UTIs. This is because they increase the amount of sugar in your urine, which can create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
- Yeast Infections: SGLT2 inhibitors can also increase the risk of yeast infections, particularly in women.
- Dehydration: You may experience dehydration due to increased urination. It’s important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
In rare cases, SGLT2 inhibitors can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Ketoacidosis: This is a serious condition that occurs when your body produces too many ketones. Symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and confusion. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
- Amputations: In people with diabetic foot ulcers, SGLT2 inhibitors may increase the risk of amputations. This is because they can reduce blood flow to the feet, which can delay wound healing.
It’s crucial to discuss any concerns or side effects you experience with your doctor. They can help you manage your treatment effectively and minimize any potential risks.
Managing Your SGLT2 Inhibitor Therapy
To manage your SGLT2 inhibitor therapy effectively, follow these guidelines:
- Take your medication as prescribed: It’s crucial to take your medication as directed by your doctor. Don’t skip doses or change the dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels using a home glucose meter. This will help you track your progress and ensure your medication is working effectively.
- Monitor your blood pressure: If your doctor has prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors for blood pressure management, regularly check your blood pressure using a home blood pressure monitor.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially during hot weather or when you’re exercising.
- Report any side effects: It’s essential to inform your doctor about any side effects you experience, especially if they are severe or persistent.
- Keep your doctor informed: Keep your doctor informed about any changes in your health, medications, or lifestyle. This will help them adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Checklist for SGLT2 Inhibitor Therapy
This checklist can help you track your blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and any side effects while on SGLT2 inhibitors.
| Date | Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) | Blood Pressure (mmHg) | Side Effects | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Comparative Analysis of SGLT2 Inhibitors
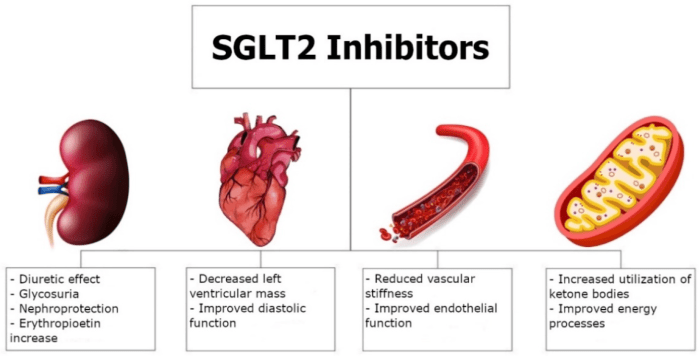
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. They work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine and lower blood sugar levels. While all SGLT2 inhibitors share this mechanism of action, they differ in their efficacy, safety profiles, and other characteristics. This section will compare and contrast different SGLT2 inhibitors to help understand their unique properties and guide the selection process for individual patients.
Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Different SGLT2 Inhibitors
The efficacy and safety profiles of SGLT2 inhibitors have been extensively studied in clinical trials.
- Canagliflozin, Dapagliflozin, Empagliflozin, and Ipragliflozin have all demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels, blood pressure, and cardiovascular risk.
- Ertugliflozin is a newer SGLT2 inhibitor that has shown promising results in clinical trials.
In terms of safety, all SGLT2 inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk of genital mycotic infections. Other potential adverse effects include urinary tract infections, dehydration, and volume depletion.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an SGLT2 Inhibitor
Several factors should be considered when selecting an SGLT2 inhibitor for a particular patient. These include:
- Efficacy: The effectiveness of the drug in lowering blood sugar levels and reducing cardiovascular risk.
- Safety: The potential side effects and drug interactions.
- Cost: The cost of the medication and the availability of insurance coverage.
- Patient preferences: The patient’s individual preferences and concerns.
Evidence Supporting the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Different Clinical Settings
SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to be effective in a variety of clinical settings, including:
- Type 2 diabetes: SGLT2 inhibitors are effective in lowering blood sugar levels and reducing cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Heart failure: SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization in patients with heart failure.
- Chronic kidney disease: SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Potential Benefits and Limitations of Each SGLT2 Inhibitor
Each SGLT2 inhibitor has its own unique set of benefits and limitations. For example:
- Canagliflozin is generally well-tolerated but may increase the risk of lower limb amputation in patients with peripheral artery disease.
- Dapagliflozin has been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes, but it may increase the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with poorly controlled diabetes.
- Empagliflozin has a favorable safety profile and has been shown to be effective in reducing cardiovascular risk, but it may be more expensive than other SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Ipragliflozin is generally well-tolerated and has a long half-life, but it may be associated with an increased risk of hypoglycemia in patients with impaired renal function.
- Ertugliflozin has shown promising results in clinical trials, but it is a newer drug with limited long-term data available.
SGLT2 inhibitors represent a powerful tool in the fight against diabetes and its associated complications. Their ability to address multiple aspects of the disease, including blood sugar control, cardiovascular risk reduction, and kidney protection, underscores their importance in personalized diabetes management. As research continues to unravel the full potential of these medications, we can anticipate even more innovative applications and improvements in the lives of individuals living with diabetes.
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications that help lower blood sugar levels by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys. They are often used in conjunction with other diabetes medications, such as statins like pravastatin , which work to lower cholesterol levels. While SGLT2 inhibitors primarily target blood sugar, their effects on kidney function and cardiovascular health are also being investigated.