Ustekinumab, a powerful immunotherapy, has emerged as a game-changer in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases like psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This targeted therapy works by selectively blocking key inflammatory pathways, offering relief for patients struggling with these debilitating conditions.
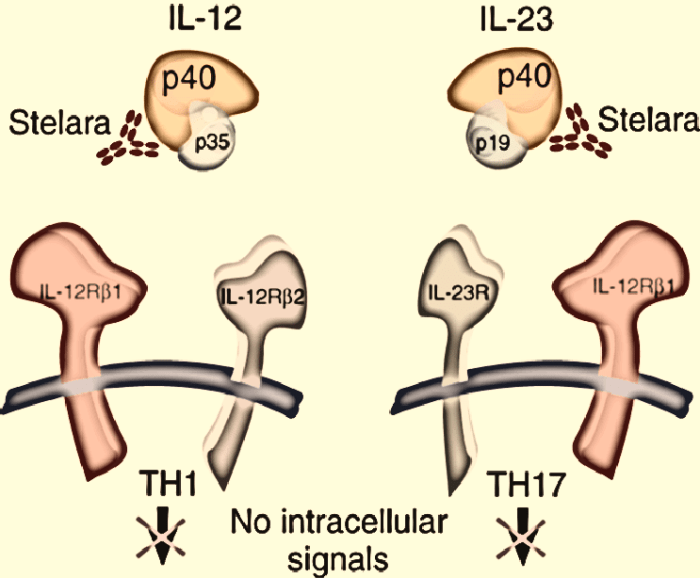
Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the p40 subunit of interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23, two cytokines that play a critical role in the development and progression of inflammatory skin and gut diseases. By inhibiting these cytokines, ustekinumab helps to reduce inflammation, suppress immune responses, and promote skin and gut healing.
Monitoring and Management of Ustekinumab Treatment
Ustekinumab therapy requires close monitoring to ensure its effectiveness and manage potential adverse effects. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for assessing treatment response, adjusting dosage, and addressing any concerns.
Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring parameters are crucial for assessing treatment response and identifying potential complications. These parameters include:
- Disease Activity: Regular assessments of disease activity using validated disease activity indices, such as the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) for psoriasis and the Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) for Crohn’s disease, are essential to track treatment effectiveness.
- Adverse Effects: Close monitoring for potential adverse effects, such as infections, infusion reactions, and autoimmune disorders, is essential. Early identification and management of these effects can minimize their impact.
- Laboratory Tests: Regular laboratory tests, including complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, and inflammatory markers, are important for monitoring overall health and detecting any potential complications.
- Immunizations: Patients receiving ustekinumab should be up-to-date on their immunizations, as the medication can suppress the immune system.
Regular Follow-Up Appointments, Ustekinumab
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for:
- Assessing Treatment Response: Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of ustekinumab therapy and adjust the dosage if necessary.
- Managing Adverse Effects: Early identification and management of adverse effects can minimize their impact and prevent complications.
- Providing Patient Education: Follow-up appointments provide opportunities for patients to receive education about their condition, treatment options, and potential side effects.
Management Strategies for Adverse Effects or Treatment Failure
If a patient experiences adverse effects or treatment failure, management strategies may include:
- Dosage Adjustment: The dosage of ustekinumab may be adjusted to minimize adverse effects or enhance treatment efficacy.
- Treatment Discontinuation: In some cases, ustekinumab therapy may be discontinued if adverse effects are severe or treatment failure is persistent.
- Alternative Therapies: If ustekinumab is ineffective or not tolerated, alternative therapies, such as other biologic agents or conventional medications, may be considered.
Cost and Accessibility of Ustekinumab
Ustekinumab is a biologic medication used to treat various inflammatory conditions, including plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. While it can be effective, the cost of ustekinumab can be a significant barrier to access for many patients. This section explores the cost of ustekinumab compared to other treatment options, factors influencing its accessibility, and the role of insurance coverage and patient assistance programs.
Cost Comparison with Other Treatment Options
The cost of ustekinumab varies depending on the specific indication, dosage, and pharmacy. However, it is generally considered a high-cost medication. It is important to note that the cost of any medication can vary depending on factors like insurance coverage, pharmacy location, and manufacturer rebates.
- Traditional Therapies: Traditional therapies for inflammatory conditions, such as topical creams, oral medications, and phototherapy, are generally less expensive than biologics like ustekinumab. However, they may not be as effective for all patients, and they may have different side effects.
- Other Biologics: There are other biologic medications available for treating inflammatory conditions, such as adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept. The cost of these medications can vary, but they are generally comparable to ustekinumab.
Factors Influencing Accessibility
Several factors can influence the accessibility of ustekinumab, including:
- Cost of Medication: The high cost of ustekinumab can be a significant barrier for many patients, particularly those without adequate insurance coverage.
- Insurance Coverage: Insurance coverage for ustekinumab can vary widely. Some insurance plans may require prior authorization or may only cover certain indications.
- Patient’s Financial Situation: The out-of-pocket costs for ustekinumab can be substantial, even with insurance coverage. This can be a challenge for patients with limited financial resources.
- Availability of Treatment Centers: Access to ustekinumab may be limited in some areas due to the availability of treatment centers that can administer the medication.
Role of Insurance Coverage and Patient Assistance Programs
Insurance coverage plays a crucial role in determining the accessibility of ustekinumab. Many insurance plans cover biologic medications, but they may have restrictions on coverage, such as requiring prior authorization or limiting the number of doses covered per year.
- Prior Authorization: Insurance companies often require prior authorization for ustekinumab, which means that patients must obtain approval from their insurance company before they can receive the medication. This process can be time-consuming and may delay treatment.
- Patient Assistance Programs: Pharmaceutical companies often offer patient assistance programs (PAPs) to help patients afford their medications. These programs may provide financial assistance, co-pay assistance, or free medication to eligible patients.
Future Directions in Ustekinumab Research
Ustekinumab has emerged as a valuable treatment option for various inflammatory conditions, but ongoing research continues to explore its potential and optimize its use. The focus of current research is on expanding its applications, developing novel formulations, and refining existing treatment strategies.
Ongoing Research Efforts
Ongoing research efforts related to ustekinumab aim to deepen our understanding of its mechanisms of action, optimize its use in existing indications, and explore its potential in new therapeutic areas.
- Clinical Trials: Numerous clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in various diseases, including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. These trials are exploring different dosing regimens, combination therapies, and long-term outcomes.
- Biomarker Studies: Researchers are investigating potential biomarkers that could predict patient response to ustekinumab and identify individuals who might benefit most from treatment. This research could lead to personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patient characteristics.
- Mechanism of Action: Ongoing studies are investigating the precise mechanisms by which ustekinumab exerts its therapeutic effects. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to the development of more targeted therapies and potentially even novel drugs that target the same pathways.
Potential New Indications and Applications
Ustekinumab’s ability to target IL-12 and IL-23, key cytokines involved in inflammation, has opened up possibilities for its use in a broader range of inflammatory conditions.
- Atopic Dermatitis: Studies are investigating the potential of ustekinumab for treating severe atopic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Early findings suggest promising results, with ustekinumab showing significant improvement in skin lesions and symptoms.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Research is exploring the use of ustekinumab for rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and pain. Preliminary studies have shown potential benefits, but further research is needed to confirm its efficacy and safety in this context.
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: Ustekinumab’s potential is being investigated in other autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. These studies are exploring the feasibility of using ustekinumab as a treatment option in these complex conditions.
Development of Novel Formulations and Delivery Methods
Efforts are underway to develop novel formulations and delivery methods for ustekinumab, aiming to improve its efficacy, convenience, and patient adherence.
- Biosimilar Development: Biosimilar versions of ustekinumab are being developed, offering potentially more affordable alternatives to the original drug. These biosimilars must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they are comparable to the original in terms of efficacy, safety, and quality.
- Long-Acting Formulations: Researchers are investigating long-acting formulations of ustekinumab that could provide sustained therapeutic effects with fewer injections. This could significantly improve patient convenience and adherence to treatment.
- Alternative Delivery Methods: Studies are exploring alternative delivery methods for ustekinumab, such as topical or oral administration. These methods could potentially offer more convenient and less invasive ways to deliver the drug.
Ustekinumab
Ustekinumab is a biologic medication used to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Crohn’s disease. It works by blocking the signaling of certain proteins that contribute to inflammation. Ustekinumab is typically administered as an injection under the skin (subcutaneously) every 8 or 12 weeks.
Ustekinumab: A Case Study
This case study illustrates the use of ustekinumab in a patient with psoriasis.
Patient Presentation:
A 35-year-old male patient presented to the dermatology clinic with a history of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis for the past 10 years. He had tried various topical treatments, including corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, but his symptoms persisted. He was experiencing significant physical and emotional distress due to the appearance of his skin lesions.
Diagnosis:
The patient was diagnosed with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis based on clinical examination and the history of his condition.
Treatment Plan:
After a thorough discussion of treatment options, the patient decided to start ustekinumab therapy. He received his first injection of ustekinumab at the clinic. The patient was monitored closely for any adverse effects and was advised to continue using his topical treatments as needed.
Outcomes:
The patient experienced a significant improvement in his psoriasis symptoms within a few weeks of starting ustekinumab therapy. His skin lesions cleared significantly, and his quality of life improved. He was able to participate in social activities and engage in hobbies without feeling self-conscious about his skin.
Challenges and Considerations:
* Cost: Ustekinumab is a biologic medication, and its cost can be a significant barrier for some patients.
* Adverse Effects: While generally well-tolerated, ustekinumab can cause some side effects, including injection site reactions, infections, and allergic reactions.
* Monitoring: Regular monitoring of patients receiving ustekinumab is crucial to assess treatment efficacy, identify any adverse effects, and ensure patient safety.
* Patient Education: It is essential to educate patients about the benefits and risks of ustekinumab therapy, as well as the importance of adhering to the treatment plan.
Conclusion:
Ustekinumab can be an effective treatment option for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. It can significantly improve skin clearance, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of ustekinumab therapy and to monitor patients closely for any adverse effects.
Ustekinumab has revolutionized the treatment landscape for psoriasis and IBD, offering a safe and effective option for patients seeking long-term disease management. Its targeted mechanism of action, favorable safety profile, and demonstrated efficacy make it a valuable tool for clinicians in achieving meaningful improvements in patient outcomes. As research continues to explore new applications and refine existing therapies, ustekinumab holds immense potential for further impacting the lives of individuals living with these chronic conditions.
Ustekinumab is a medication used to treat plaque psoriasis, a skin condition causing red, scaly patches. While ustekinumab targets the immune system, it’s important to note that other medications, such as avonex , work differently by modulating the immune system’s response to the central nervous system. Ustekinumab is typically administered via injection, and its effectiveness can vary depending on individual factors.